# 对数据结构的认知
学习数据结构,可以说是在修炼内功,一些总结些常见的数据结构
# 栈和队列
首先,栈和队列都是 线性储存数据 的一种方式,且是按照某种规则
- 栈 (先进后出)
- 队列 ( 先进先出 )
# 栈的封装(基于数组)
JavaScript 中没有这种数据结构,我们需要自己封装
// 实现栈,基于数组
class Z {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
// 添加数据 入栈
push(item) {
this.items.push(item);
}
// 删除数据 出栈
pop() {
this.items.pop();
}
// 判断是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
// 判断栈的长度
len() {
return this.items.length;
}
}
# 队列的封装(基于数组)
我们会发现,栈和队列代码其实差不多,就是出栈的方式不同
class D {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
// 添加数据 入栈
push(item) {
this.items.push(item);
}
// 删除数据 出栈
pop() {
this.items.shift();
}
// 判断是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
// 判断栈的长度
len() {
return this.items.length;
}
}
# 链表
# 链表的优势
如果说链表的优势,那就要说说栈和队列的这种数据结构的缺点了
因为 栈和队列 是居于数组的,其实数组在 查找 数据和 修改 数据的时候效率还可以,但是在 添加数据及删除数据 时,效率很低。
这是因为在向数组里面添加和删除数据时,数组的 下标 都要变化,尤其是当数组的数据量很大,添加和删除数组的第一个元素,效率问题尤为突出
而链表这种数据结构,就是来解决这个问题的
# 单项链表
单项链表是一种 链式存储的线性表,是由一组节点组成的集合,每一个节点都存储了下一个节点的地址;指向另一个节点的引用叫链;和数组中的元素内存地址是连续的相比,链表中的所有元素的内存地址不一定是连续的,如图:
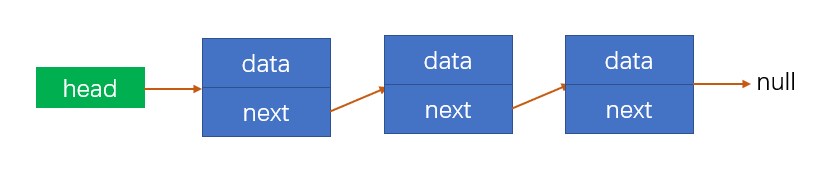
# 单项链表封装
function linkedList() {
//链表的节点类
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
this.head = null; // 链表的hede 可以理解为指针
this.length = 0; //链表的长度
// 添加方法
linkedList.prototype.append = function(data) {
var newNode = new Node(data);
// 判断现在的链表是不是空
if (this.length == 0) {
// 添加的是第一个节点
this.head = newNode;
} else {
// 不是第一个节点,找到最后一个节点,在其后面追加节点
var current = this.head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next; //一直往下找
}
// 追加最后一个节点
current.next = newNode;
}
this.length++;
};
// 插入方法,可以把数据插入到链表的任何地方
linkedList.prototype.insert = function(position, data) {
// 对 position 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) {
return false;
}
var newNode = new Node(data);
// 判断是不是插入到第一个
if (position == 0) {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
} else {
var index = 0;
var current = this.head;
var previous = null; // 记录上一个节点
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
newNode.next = current;
previous.next = newNode;
}
this.length++;
return true;
};
// 获取对应位置上的数据
linkedList.prototype.get = function(position) {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) {
return null;
}
var current = this.head;
var index = 0;
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next;
}
return current.next;
};
// 获取对应数据的下标值
linkedList.prototype.indexOf = function(data) {
var current = this.head;
var index = 0;
while (current) {
if (current.data == data) {
return index;
}
current = current.next;
index++;
}
return -1;
};
// 更新方法
linkedList.prototype.updata = function(position, data) {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) {
return false;
}
var current = this.head;
var index = 0;
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next;
}
current.data = data;
return true;
};
// 根据位置 删除元素
linkedList.prototype.removeAt = function(position) {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) {
return false;
}
// 删除第一个
if (position == 0) {
this.head = this.head.next;
} else {
var current = this.head;
var previous = null;
var index = 0;
while (index++ < position) {
position = current;
current = current.next;
}
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.length -= 1;
return true;
};
// 字符串化
linkedList.prototype.toString = function() {
var current = this.head;
var listString = "";
// 循环获取一个个节点
while (current) {
listString += current.data + " ";
current = current.next;
}
return listString;
};
}
# 双向链表
简单来说,在单项链表中,一个节点只有一个指针且指向下一个节点。所以在单项链表中,我们要想查找一个节点的上一个节点就比较困难(只能从头遍历)
而双向链表就是做这个事情,之所以为双向链表,是因为在双向链表中,每个节点两个指针,一个是指向上一个节点的数据,另一个指向下一个节点的数据:如下图所示:
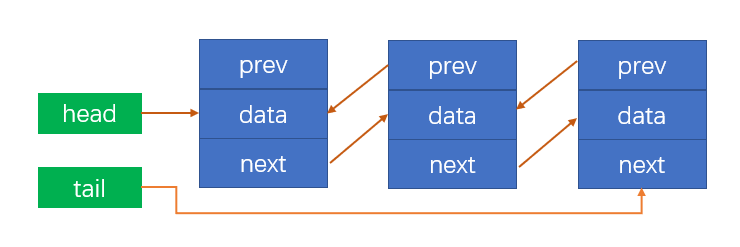
# 双向链表封装
// 双向链表
function DoublyList() {
this.head = null; //指针 指向第一个
this.tail = null; // 指针 指向最后一个
this.length = 0; // 列表的长度
// 内部节点类
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
// 插入到链表的尾部
DoublyList.prototype.append = function(data) {
// 判断是否添加的第一个节点
var newNode = new Node(data);
if (this.length == 0) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length += 1;
};
// 插入
DoublyList.prototype.insert = function(position, data) {
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
var newNode = new Node(data);
// 插入的节点是第一个节点
if (this.length == 0) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
if (position == 0) {
this.head.prev = newNode;
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
} else if (position == this.length) {
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
var current = this.head;
var index = 0;
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next;
}
// 更改对应指针指向
newNode.next = current;
newNode.prev = current.prev;
current.prev.next = newNode;
current.prev = newNode;
}
this.length += 1;
};
// 获取对应下标的数据
DoublyList.prototype.get = function(position) {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return false;
// 获取元素
var current = this.head;
var index = 0;
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next;
}
return current.data;
};
// 获取对应值的下标
DoublyList.prototype.indexOf = function(data) {
var current = this.head;
var index = 0;
while (current) {
if (current.data == data) {
return index;
}
index++;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
};
// 根据下标更新
DoublyList.prototype.updata = function(position, newData) {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return false;
// 获取元素
var current = this.head;
var index = 0;
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next;
}
current.data = newData;
return true;
};
// 根据下标删除
DoublyList.prototype.removeAt = function(position) {
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
if (this.length == 1) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
if (position == 0) {
this.head.next.prev = null;
this.head = this.head.next;
} else if (position == this.length - 1) {
this.tail.prev.next = null;
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
} else {
var index = 0;
var current = this.head;
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next;
}
current.prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
};
DoublyList.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.bacckwardToString();
};
// 从后向前遍历
DoublyList.prototype.forwardToString = function() {
var current = this.tail;
var resString = "";
while (current) {
current = current.prev;
resString += current.data + " ";
}
return resString;
};
// 从前向后遍历
DoublyList.prototype.bacckwardToString = function() {
var current = this.head;
var resString = "";
while (current) {
current = current.next;
resString += current.data + " ";
}
return resString;
};
}
# 二叉树
二叉树的一个节点 Node 由 data,left,right 组成,data 保存本节点的值,left 指向左节点,right 指向右节点。二叉树有一个特殊性:相对本节点较小的值保存在左节点,相对本节点较大的值保存在右节点,该特性能让查值效率提高
# 特点
- 每个节点只有 left 和 right
- left 值小于 right 值
- 整个数的最小值在最左边,最大值在最右边
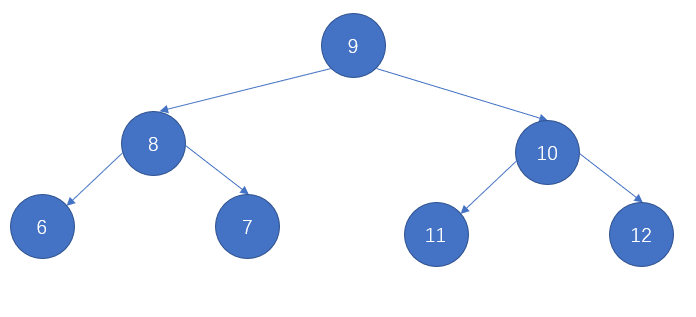
# 二叉树封装
function BinSer() {
function Node(key) {
this.key = key;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
// 属性
this.root = null;
// 方法
// 插入数据
BinSer.prototype.insert = function(key) {
// 1.创建一个节点
var newNode = new Node(key);
// 2.判断根节点是否有值
if (this.root == null) {
this.root = newNode;
} else {
// 有根节点
this.insertNode(this.root, newNode);
}
};
BinSer.prototype.insertNode = function(node, newNode) {
// node 被比较的节点
if (newNode.key < node.key) {
// 向左查找
if (node.left == null) {
node.left = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode);
}
} else {
// 向右查找
if (node.right == null) {
node.right = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode);
}
}
};
// 先序遍历
BinSer.prototype.preOrder = function(handler) {
this.preOrderNode(this.root, handler);
};
BinSer.prototype.preOrderNode = function(node, handler) {
if (node != null) {
handler(node.key);
this.preOrderNode(node.left, handler);
this.preOrderNode(node.right, handler);
}
};
BinSer.prototype.max = function() {
var node = this.root;
var key = null;
while (node != null) {
node = node.right;
key = node.right;
}
return key;
};
BinSer.prototype.min = function() {
var node = this.root;
var key = null;
while (node != null) {
node = node.left;
key = node.left;
}
return key;
};
}
# 哈希表
# 什么是哈希表
网上解释:Hash 表也称散列表,也有直接称为哈希表,是一种根据关键字值(key-value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。它是通过把关键字映射到数组的下标来加快查找速度。普通的数据结构中查找某一个关键字通常需要遍历整个数据结构,时间复杂度 O(n),而哈希表只需要 O(1)的时间级
自己解释: 哈希表类似与我们现在的对象,是通过 key 去得到对应的 value
# 需要思考的问题
怎么合理的去规定一个容器,然后按照 key-value 的方式去存放这些数据
比如 我现在有 1000 个员工(员工包括姓名,电话,工作等信息)现在怎么把这些员工的信息合理的储存起来?(当然用 json 存储时最合理的,我们可以把 json 看作时一个语法糖那计算机底层时怎么存的呢)
在计算机中,我们首先要申请一个容器去存放这些数据,比如我就申请 1000 个地址,就会有以下问题:
- 那要是再添加员工了怎么办呢?
- 如果公司裁员,裁掉了 900 个员工,那剩下 10 个员工用 1000 个地址存放是不是很浪费?
那么 哈希函就是解决这种情况的一种数据结构
# 哈希函数
哈希函数做了一个事情, 就是把数据 均匀 的分布在一定长度的容器里,从而减少重复的概率
function hashFunc(str, size) {
var hashCode = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
hashCode = 37 * hashCode + str.charCodeAt(i);
}
var index = hashCode % size;
return index;
}
console.log(hashFunc("aa", 10));
console.log(hashFunc("bb", 10));
console.log(hashFunc("cc", 10));
// 2 6 4
但是即使如此,当我们再向里面添加数据时还是有可能重复,一把有两种解决方案
开放地址法 开发地址法中,若数据项不能直接存放在由哈希函数所计算出来的数组下标时,就要寻找其他的位置。分别有三种方法:线性探测、二次探测以及再哈希法
也就是说,当插入数据时,如果得知某个地址被占用,就去找下一个没有被占用的地址存放数据链地址法 链地址法中,装填因子(数据项数和哈希表容量的比值)与开放地址法不同,在链地址法中,需要有 N 个单元的数组中转入 N 个或更多的数据项,因此装填因子一般为 1,或比 1 大(有可能某些位置包含的链表中包含两个或两个以上的数据项)。
也就是说,每一个地址是一个数组,把相同下标的数据都存放再一个地址,当查找数据时先按照下标查找到对应的地址,再从地址的数组中线性遍历这里我们实现下链地址法的封装
function HashTable() {
this.storage = [];
this.count = 0;
this.limit = 7;
HashTable.prototype.hashFunc = function(str, size) {
var hashCode = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
hashCode = 37 * hashCode + str.charCodeAt(i);
}
var index = hashCode % size;
return index;
};
// 插入,修改
HashTable.prototype.put = function(key, value) {
// 根据key 获取对应的index
var index = this.hashFunc(key, this.limit);
// 根据index 取数据
var bucket = this.storage[index];
// 判断该bucket 是否为空
if (bucket == null) {
bucket = [];
this.storage[index] = bucket;
}
// 判断是不是修改数据
for (var i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
var tuple = bucket[i];
if (tuple[0] == key) {
tuple[1] = value;
}
}
// 添加
bucket.push([key, value]);
this.count += 1;
};
// 获取方法
HashTable.prototype.get = function(key) {
var index = this.hashFunc(key, this.limit);
var bucket = this.storage[index];
if (bucket == null) {
return null;
}
for (var i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
var tuple = bucket[i];
if (tuple[0] == key) {
return tuple[1];
}
}
return null;
};
// 删除方法
HashTable.prototype.remove = function(key) {
var index = this.hashFunc(key, this.limit);
var bucket = this.storage[index];
if (bucket == null) {
return false;
}
for (var i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
var tuple = bucket[i];
if (tuple[0] == key) {
bucket.splice(i, 1);
this.count -= 1;
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
}
数组扁平化 →